6 月 . 25, 2024 04:15 Back to list
Hepatitis C Diagnostic Testing A Closer Look at Screening Methods
Navigating the Terrain of Hepatitis C Testing
Hepatitis C, a viral infection that targets the liver, is a silent but formidable adversary to global health. The virus can lead to chronic inflammation and may progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer if left untreated. Given its potentially insidious nature, understanding the importance and mechanics of Hepatitis C testing is imperative for early detection and intervention.
The first line of defense against Hepatitis C is awareness. High-risk groups such as intravenous drug users, those with multiple sexual partners, and individuals who have received blood transfusions or organ transplants before 1992 should be particularly vigilant. Symptoms of Hepatitis C are often vague and may not appear until the virus has been wreaking havoc on the liver for years. Thus, regular testing becomes a critical strategy in managing this disease.
Two main types of tests are utilized for Hepatitis C screening Antibody tests and molecular tests. The antibody test, typically administered first, looks for antibodies in the blood that indicate a response to the Hepatitis C virus. A positive result suggests that the person has been infected at some point; however, it does not distinguish between current and past infections.
To confirm an active infection, a molecular test, also known as a viral load test, is employed. This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time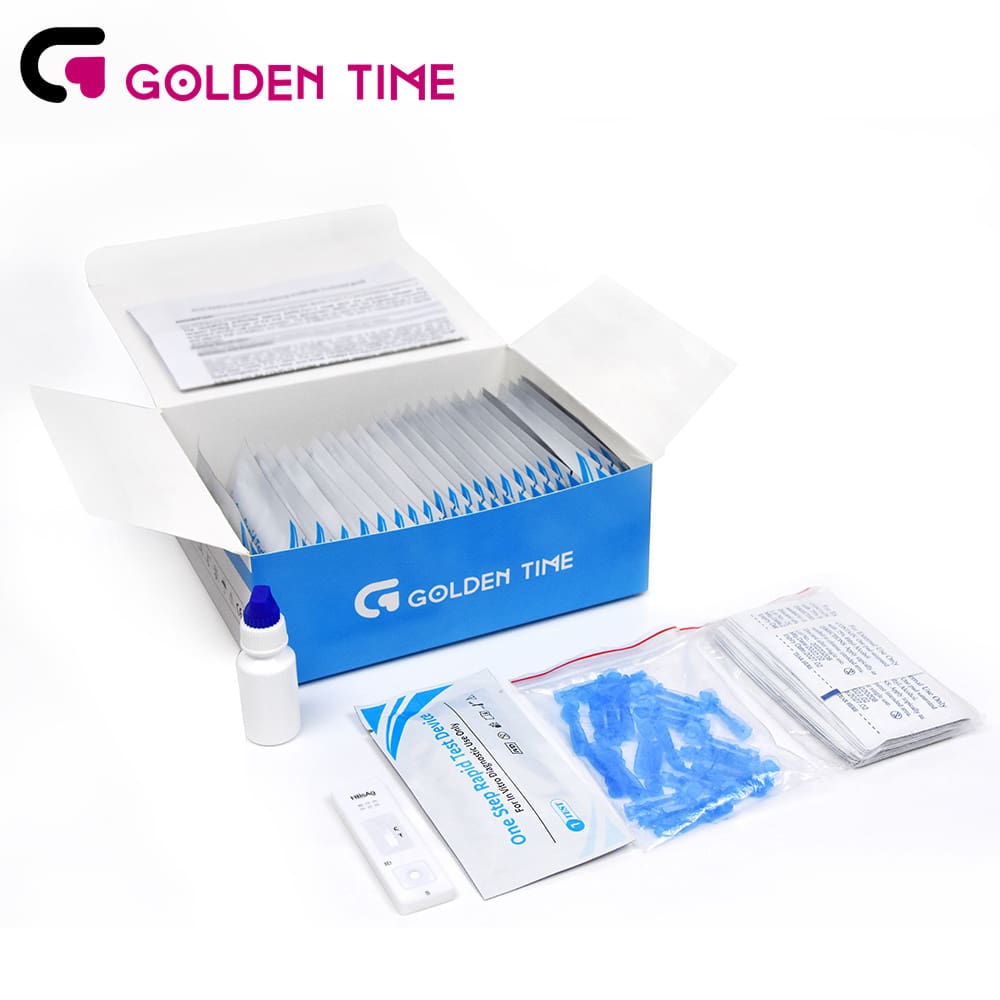 This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time
This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time hepatitis c test.
In terms of accessibility, Hepatitis C testing has become more widespread and less invasive. Blood draws are the standard method, but newer technologies allow for rapid and even home-based testing, reducing barriers to diagnosis.
Despite these advancements, stigma and lack of awareness remain significant hurdles in the fight against Hepatitis C. Public health initiatives aim to educate the public about the importance of testing, especially among populations with a higher prevalence of the disease.
Treatment for Hepatitis C has made remarkable strides with the advent of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). These medications can cure more than 95% of cases when taken as prescribed. Yet, without testing, the opportunity for cure is missed.
In conclusion, Hepatitis C testing is a vital component of the broader strategy to control and eradicate this disease. As technology continues to evolve and knowledge spreads, it is hoped that more individuals will come forward for testing, thereby increasing the chances of successful treatment outcomes and ultimately diminishing the global burden of Hepatitis C.
hepatitis c test.
In terms of accessibility, Hepatitis C testing has become more widespread and less invasive. Blood draws are the standard method, but newer technologies allow for rapid and even home-based testing, reducing barriers to diagnosis.
Despite these advancements, stigma and lack of awareness remain significant hurdles in the fight against Hepatitis C. Public health initiatives aim to educate the public about the importance of testing, especially among populations with a higher prevalence of the disease.
Treatment for Hepatitis C has made remarkable strides with the advent of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). These medications can cure more than 95% of cases when taken as prescribed. Yet, without testing, the opportunity for cure is missed.
In conclusion, Hepatitis C testing is a vital component of the broader strategy to control and eradicate this disease. As technology continues to evolve and knowledge spreads, it is hoped that more individuals will come forward for testing, thereby increasing the chances of successful treatment outcomes and ultimately diminishing the global burden of Hepatitis C.
 This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time
This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time This test detects and measures the actual amount of virus in the blood, helping healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment and monitor the effectiveness of therapy over time hepatitis c test.
In terms of accessibility, Hepatitis C testing has become more widespread and less invasive. Blood draws are the standard method, but newer technologies allow for rapid and even home-based testing, reducing barriers to diagnosis.
Despite these advancements, stigma and lack of awareness remain significant hurdles in the fight against Hepatitis C. Public health initiatives aim to educate the public about the importance of testing, especially among populations with a higher prevalence of the disease.
Treatment for Hepatitis C has made remarkable strides with the advent of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). These medications can cure more than 95% of cases when taken as prescribed. Yet, without testing, the opportunity for cure is missed.
In conclusion, Hepatitis C testing is a vital component of the broader strategy to control and eradicate this disease. As technology continues to evolve and knowledge spreads, it is hoped that more individuals will come forward for testing, thereby increasing the chances of successful treatment outcomes and ultimately diminishing the global burden of Hepatitis C.
hepatitis c test.
In terms of accessibility, Hepatitis C testing has become more widespread and less invasive. Blood draws are the standard method, but newer technologies allow for rapid and even home-based testing, reducing barriers to diagnosis.
Despite these advancements, stigma and lack of awareness remain significant hurdles in the fight against Hepatitis C. Public health initiatives aim to educate the public about the importance of testing, especially among populations with a higher prevalence of the disease.
Treatment for Hepatitis C has made remarkable strides with the advent of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). These medications can cure more than 95% of cases when taken as prescribed. Yet, without testing, the opportunity for cure is missed.
In conclusion, Hepatitis C testing is a vital component of the broader strategy to control and eradicate this disease. As technology continues to evolve and knowledge spreads, it is hoped that more individuals will come forward for testing, thereby increasing the chances of successful treatment outcomes and ultimately diminishing the global burden of Hepatitis C. Latest news
-
Early Pregnancy Test Kits Accurate & Fast Results Bulk Order Now
NewsMay.30,2025
-
Buy OPK Tests for Pregnancy Detection Bulk Supplier Discounts
NewsMay.30,2025
-
Buy OPK Tests for Pregnancy Detection Bulk Supplier Discounts
NewsMay.30,2025
-
Best At Home H Pylori Test Kits Accurate, Fast & FDA-Certified
NewsMay.29,2025
-
Accurate Syphilis Test Kits Trusted Suppliers & Manufacturers
NewsMay.29,2025
-
Wholesale Stool Occult Blood Test Kits Bulk Supplier Pricing
NewsMay.29,2025

